baseer
بصير (Baseer)
بصير (Baseer) is a modular, extensible binary analysis framework written in C. It allows developers to inspect, disassemble, debug, and decompile binary files using a flexible callback system. Baseer identifies file formats using magic numbers and executes corresponding handlers dynamically.
⚠️ Note: This project is still under development and may change frequently.
Architecture
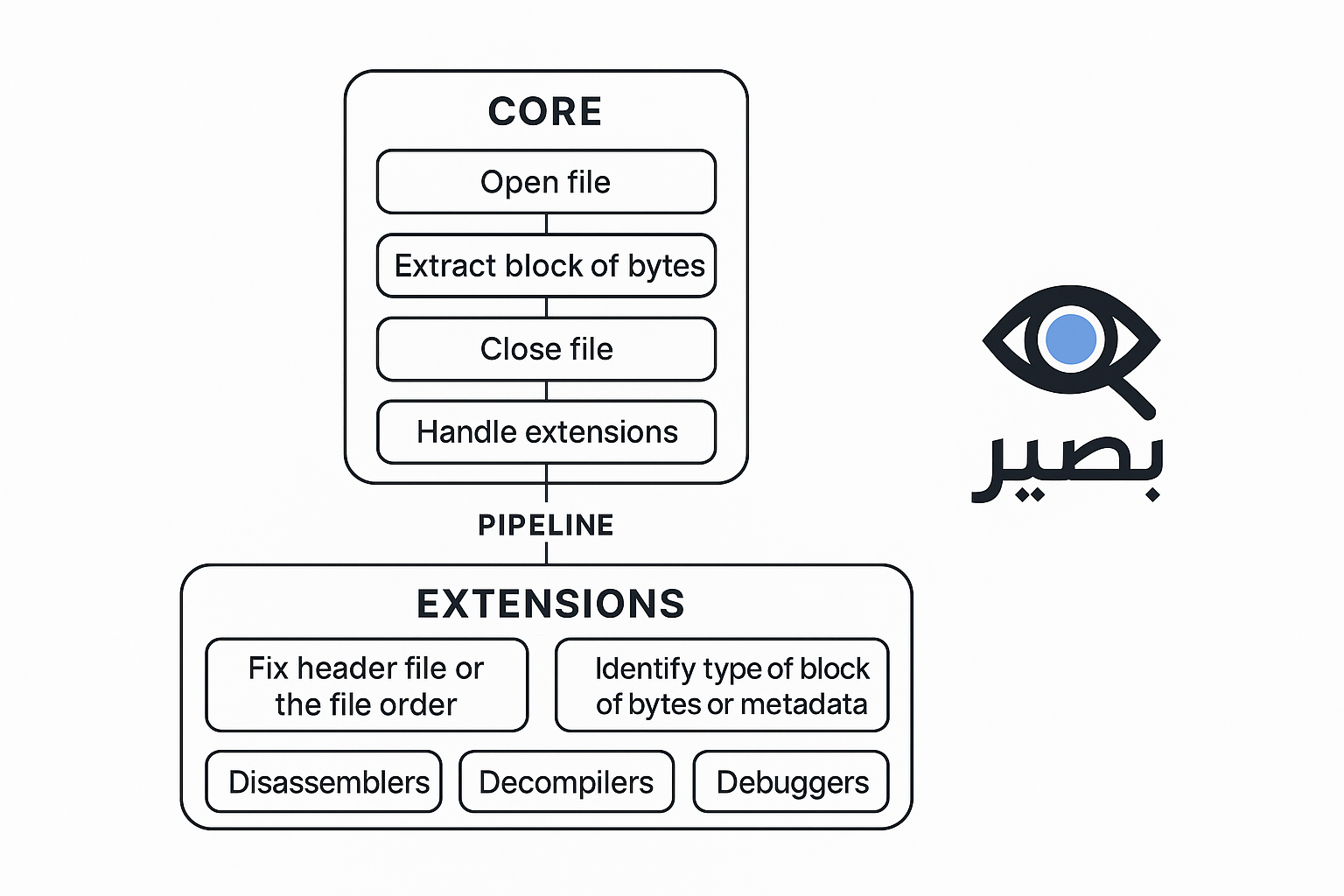
1. Core
The Core handles the essential operations:
- Open File: Read files in raw byte format.
- Extract Byte Blocks: load block of bytes into memory.
- Close File: Release resources when done.
- Handle Extensions: Load and manage various extensions.
- Manage Pipeline: Pass byte blocks through extensions sequentially or in parallel.
2. Extensions
Extensions add advanced capabilities:
- Fix Header: Repair file headers or order.
- Identify Block Type: Detect byte block type or metadata.
- Disassembler: Convert binaries to assembly instructions.
- Decompiler: Convert binaries to readable source code.
- Debugger: Dynamically monitor and analyze files.
Baseer in details
Baseer is designed around a callback tree. Each file format (e.g., ELF, TAR, etc.) is represented by a branch that defines its own callbacks. Callbacks can perform operations such as reading metadata, disassembling, debugging, or decompiling.
Baseer Architecture Diagram
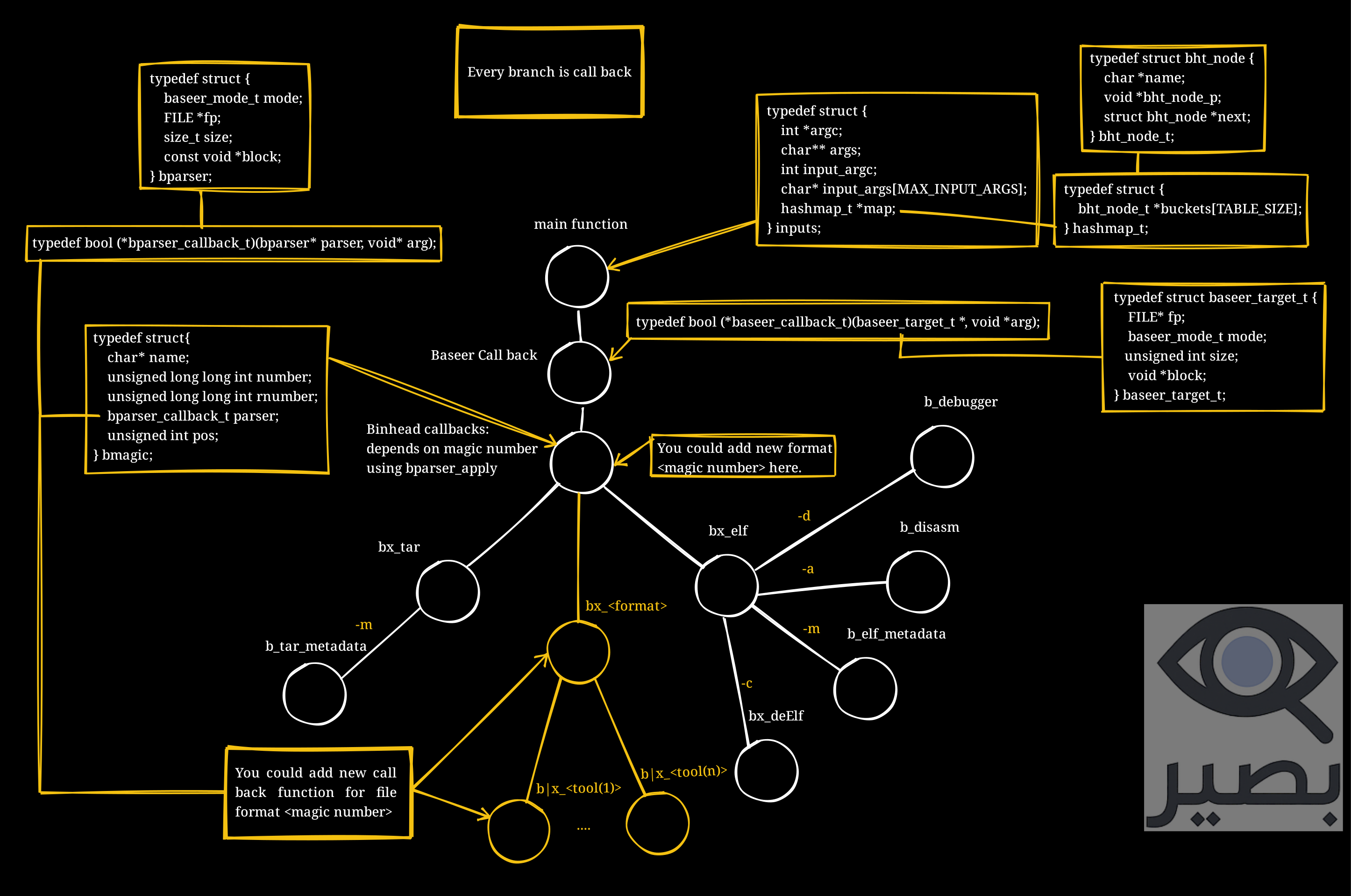
Key Concepts
bparser— the main parser structure that holds file information.bmagic— defines a magic number, the file type name, and the function callback used for parsing.inputs— holds runtime arguments and a hashmap for communication between callbacks.bparser_apply()— dispatches the execution of a callback for a given format.- Callbacks (
bx_<format>) — per-format handler (e.g.,bx_elf,bx_tar) that interprets command-line flags. - Tools (
b_<tool>) — actions executed by callbacks, such asb_debugger,b_disasm,b_elf_metadata, etc.
Each branch in the diagram represents a callback path from the main function → Baseer callback → format handler → specific tools.
Libraries Used
-
udis86: Used for disassembling x86 and x64 architecture binaries.
GitHub Repository -
RetDec: Used as the decompiler for translating binaries into a higher-level representation.
GitHub Repository
Build Instructions
Baseer uses a standard Makefile for compilation.
Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/thxa/baseer.git
cd baseer
Build Baseer
cmake CMakeLists.txt
make
Run Baseer on a binary
./build/baseer <target-file> -m
Compile and analyze file
- 64 bit
cmake CMakeLists.txt && make && ./build/baseer examples/64bit_x86_64 -m | less -r - 32 bit
cmake CMakeLists.txt && make && ./build/baseer examples/32bit_x86 -m | less -r
Requirements
- GCC
- Linux environment (recommended)
- make build system
Install Baseer
Installation on Arch Linux
You can install Baseer from the AUR using an AUR helper like yay:
yay -S baseer
Make sure you have an AUR helper installed (e.g.,
yay,paru) before running the command.
Uninstallation
To remove Baseer, use:
pacman -Rs baseer
Install from Source
To install Baseer from source:
cmake CMakeLists.txt && make install
To uninstall:
cmake CMakeLists.txt && make uninstall
Usage
Analyze a file using one of the following modes:
- Show metadata:
baseer <file> -m - Disassemble:
baseer <file> -a - Launch debugger:
baseer <file> -d - Launch REPL:
baseer -i
Features
- Written in C for speed and low-level control.
- Language-agnostic: works with files from any programming language.
- Modular and extensible architecture.
- Supports complex analysis pipelines.
- Easy API for creating new extensions.
How Baseer Works
When you run Baseer with a target file, it:
- Reads the file header and detects its magic number.
- Searches the
bmagicarray for a match. - Calls the corresponding callback (
bx_<format>) to handle the file. - Executes tools (
b_<tool>) depending on command-line flags (e.g.,-mfor metadata,-afor disassembly,-dfor debugging).
Example of the format registration:
bmagic magics[] = {
{"ELF", ELF_MAGIC, reverse_bytes(ELF_MAGIC), bx_elf, 0},
{"TAR", TAR_MAGIC, reverse_bytes(TAR_MAGIC), bx_tar, 257},
// {"PDF", PDF_MAGIC, reverse_bytes(PDF_MAGIC), NULL, 0},
// {"PNG", PNG_MAGIC, reverse_bytes(PNG_MAGIC), NULL, 0},
// {"ZIP", ZIP_MAGIC, reverse_bytes(ZIP_MAGIC), NULL, 0},
// {"Mach-o", MACHO_MAGIC, reverse_bytes(MACHO_MAGIC), NULL, 0},
};
Example: ELF Extensions
Below is an example of an already built extension for ELF .
bool bx_elf(bparser* parser, void *arg)
{
int argc = *((inputs*)arg)->argc;
char** args = ((inputs*)arg)->args;
for (int i = 2; i < argc; i++) {
if (strcmp("-m", args[i]) == 0)
bparser_apply(parser, print_meta_data, arg);
else if (strcmp("-a", args[i]) == 0)
bparser_apply(parser, print_elf_disasm, arg);
else if (strcmp("-d", args[i]) == 0)
bparser_apply(parser, b_debugger, arg);
else if (strcmp("-c", args[i]) == 0)
bparser_apply(parser, decompile_elf, arg);
else
fprintf(stderr, "[!] Unsupported flag: %s\n", args[i]);
}
return true;
}
Adding New Formats
Baseer is built to be easily extended. To add a new format (e.g., PDF, PNG, ZIP):
- Create a new file in
modules/<format>/bx_<format>.c. - Define your format callback (
bx_<format>). - Implement your tools (e.g.,
b_<tool1>,b_<tool2>). - Register your format in the
bmagicarray. - Rebuild Baseer with make.
See CONTRIBUTING.md for a detailed guide.
Supported File Types (Magic Numbers)
Use this checklist to see which file types Baseer can currently handle:
- ELF -
7F 45 4C 46(Executable and Linkable Format) - TAR -
75 73 74 61 72(TAR archive) - PDF -
25 50 44 46(Portable Document Format) - PNG -
89 50 4E 47 0D 0A 1A 0A(Portable Network Graphics) - JPEG -
FF D8 FF(JPEG image) - GIF -
47 49 46 38(Graphics Interchange Format) - ZIP -
50 4B 03 04(ZIP archive) - RAR -
52 61 72 21 1A 07 00(RAR archive) - 7Z -
37 7A BC AF 27 1C(7-Zip archive) - EXE/DOS MZ -
4D 5A(Windows executable) - Mach-O -
CF FA ED FE(Mac OS X executable) - TIFF -
49 49 2A 00/4D 4D 00 2A(Tagged Image File Format) - MP3 -
49 44 33(MP3 audio) - WAV -
52 49 46 46(Waveform Audio File) - BMP -
42 4D(Bitmap image) - ISO -
43 44 30 30 31(ISO 9660 CD-ROM image) - GZIP -
1F 8B(GZIP compressed) - FLAC -
66 4C 61 43(Free Lossless Audio Codec) - MIDI -
4D 54 68 64(MIDI sound file) - Microsoft Office (OLE) -
D0 CF 11 E0 A1 B1 1A E1(Word, Excel, PowerPoint) - Android APK -
50 4B 03 04(ZIP-based APK archive) - VMware Disk (VMDK) -
4B 44 4D(Virtual Machine Disk) - WebAssembly -
00 61 73 6D(WASM binary) - SQLite -
53 51 4C 69 74 65 20 66 69 6C 65(SQLite database) - XZ -
FD 37 7A 58 5A 00(XZ compressed) - CAB -
4D 53 43 46(Microsoft Cabinet file) - LZ4 -
04 22 4D 18(LZ4 Frame Format)
This checklist is based on the Wikipedia list of file signatures. You can extend Baseer to support more types in the future.